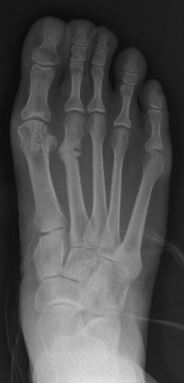
What is a “hairline fracture”?
“Hairline fractures” are actually what we call stress fractures which simply means the bone cracks (or fractures) under stress. Bones are able to absorb limited amounts of stress and strain that is placed upon them because they are rigid structures, unlike soft tissues which are more flexible. When more stress or strain is place on a bone, it may react and cause either irritation (bone bruise), inflammation (bone marrow edema) or fracture. Most commonly, these fractures appear very slight or like a strand of hair giving them the common name of a “hairline fracture”.
Stress fractures are common in weight bearing bones, such as the bones of the foot and the tibia. They are usually caused by constant and repetitive stress and strain to the bone but may be caused by an acute trauma. Stress fractures may occur from overuse, repetitive athletic activities and even due to bone alignment and foot deformities. High impact sports such as basketball, running and even ballet place someone at risk for a stress fracture. Individuals with osteoporosis and/or deficiencies in Vitamin D and Calcium are at greater risk for fractures. Carrying excess body weight can also stress a bone.
Unlike full or complete fractures due to trauma, stress fractures often do not show up on x-rays initially. Pain is generally vague and swelling is often in the area but not always. Occasionally, MRI or CT Scans are used to diagnose a stress fracture, but the findings rarely change the initial treatment so they are not usually needed. Radiographs (x-rays) will show healing of the bone as healing progresses.
The treatment for stress fractures is to rest the bone and control the abnormal forces on the bone. This may mean a cast, a walking boot or surgical shoe. Healing will be monitored with x-rays and by the improvement of clinical symptoms. It often takes a bone four to six weeks to heal enough to withstand forces placed on it. If a bone were to be subjected to similar stress too early, it could easily re-fracture. Generally, we tell patients to plan on at least 8 weeks without athletic activities after a stress fracture. There are ways to speed up healing of bones as well as soft tissues but immobilization is always necessary to some degree.